Informatik - Software und System Engineering
Kontakt
Worum geht's?
Steige ein in die Welt der Spitzentechnologie mit unserem Masterstudiengang Informatik - Software und System Engineering. Dieser Studiengang ist deine Eintrittskarte in eine Karriere, die an der Spitze technologischer Innovationen steht. Mit einem Curriculum, das auf die aktuellen und zukünftigen Bedürfnisse der Industrie zugeschnitten ist, wirst du zu einem:r führenden Experten:in in der Entwicklung und Implementierung von hochwertiger Software und robusten Systemen.
Wähle aus einer breiten Palette von Wahlpflichtfächern, um deine Kenntnisse zu vertiefen und zu spezialisieren:
- Advanced Digital IC Design: Tauche ein in die Welt des integrierten Schaltungsdesigns und lerne, wie du die nächste Generation von Mikrochips z. B. mit Open-Source Tools wie Yosys gestalten kannst.
- Advanced Security Engineering: Werde zum:r Verteidiger:in gegen Cyber-Bedrohungen, indem du lernst, wie man resistente Sicherheitsarchitekturen auf Basis moderner Kryptographie und operativen Sicherheitsmaßnahmen entwirft und implementiert.
- Internet of Things: Erforsche die vernetzte Welt und entwickele innovative Lösungen für intelligente Geräte und Systeme.
- Model-Driven Engineering und Low-Code Plattformen: Beschleunige die Softwareentwicklung mit modernen Ansätzen des Model-Driven Engineering und Low-Code-Plattformen.
- Programming Language Foundations: Vertiefe dein Verständnis der Grundlagen und Konzepte hinter Programmiersprachen, um effizientere und zuverlässigere Software zu erstellen.
- Reliable Software: Stelle sicher, dass deine Software unter allen Bedingungen funktioniert, indem du lernst, wie man zuverlässige und fehlertolerante Systeme entwickelt.
Mit diesen spezialisierten Fächern wirst du nicht nur dein Wissen erweitern, sondern auch praktische Erfahrungen sammeln, die dir in deiner Karriere einen entscheidenden Vorteil verschafft. Unser Masterstudiengang bietet dir die perfekte Kombination aus Theorie und Praxis, unterstützt von erfahrenen Dozent:innen und modernsten Laboren. Beginne heute ein Studium bei uns und forme die Zukunft der Informatik!
Dieser Studiengang kann auf Antrag auch in Teilzeit studiert werden.
Was brauche ich?
- Der Studiengang setzt einen Bachelorabschluss in einem der Informatikstudiengänge an der Hochschule RheinMain voraus oder einen Abschluss eines vergleichbaren Informatikstudiengangs einer anderen Hochschule mit min. 50 % - 65 % Informatikanteil, entsprechend der Empfehlungen der Gesellschaft für Informatik e. V.
- Im ersten berufsqualifizierenden Studienabschluss ist eine Gesamtnote von mindestens gut (2,5) erforderlich.
- Da Lehrveranstaltungen ganz oder teilweise in englischer Sprache angeboten werden können, werden ausreichende Kenntnisse der englischen Sprache (Niveau B2 gemäß dem Common European Framework of Reference for Languages) vorausgesetzt. Ein gesonderter Nachweis ist nicht erforderlich.
Was kann ich damit machen?
Den Absolvent:innen steht sowohl der akademische Arbeitsmarkt im Bereich der Wissenschaft offen als auch der nichtakademische Arbeitsmarkt in der freien Wirtschaft und der öffentlichen Verwaltung. Dabei ist die Einsatzbreite sehr groß, da das Studium nicht an einem bestimmten Berufsbild ausgerichtet ist.
Als Führungspersönlichkeiten sind die Absolvent:innen in der Lage, den digitalen Wandel in Unternehmen und Organisationen technisch und konzeptionell verantwortungsvoll zu gestalten.
Beispiele für Beschäftigungsmöglichkeiten sind: Tätigkeiten als IT-Sicherheits-Experte:in, Software Architekt:in, Network Development Engineer, Embedded Software Engineer, Cloud DevSecOps Engineer, Data Scientist oder System Engineer.
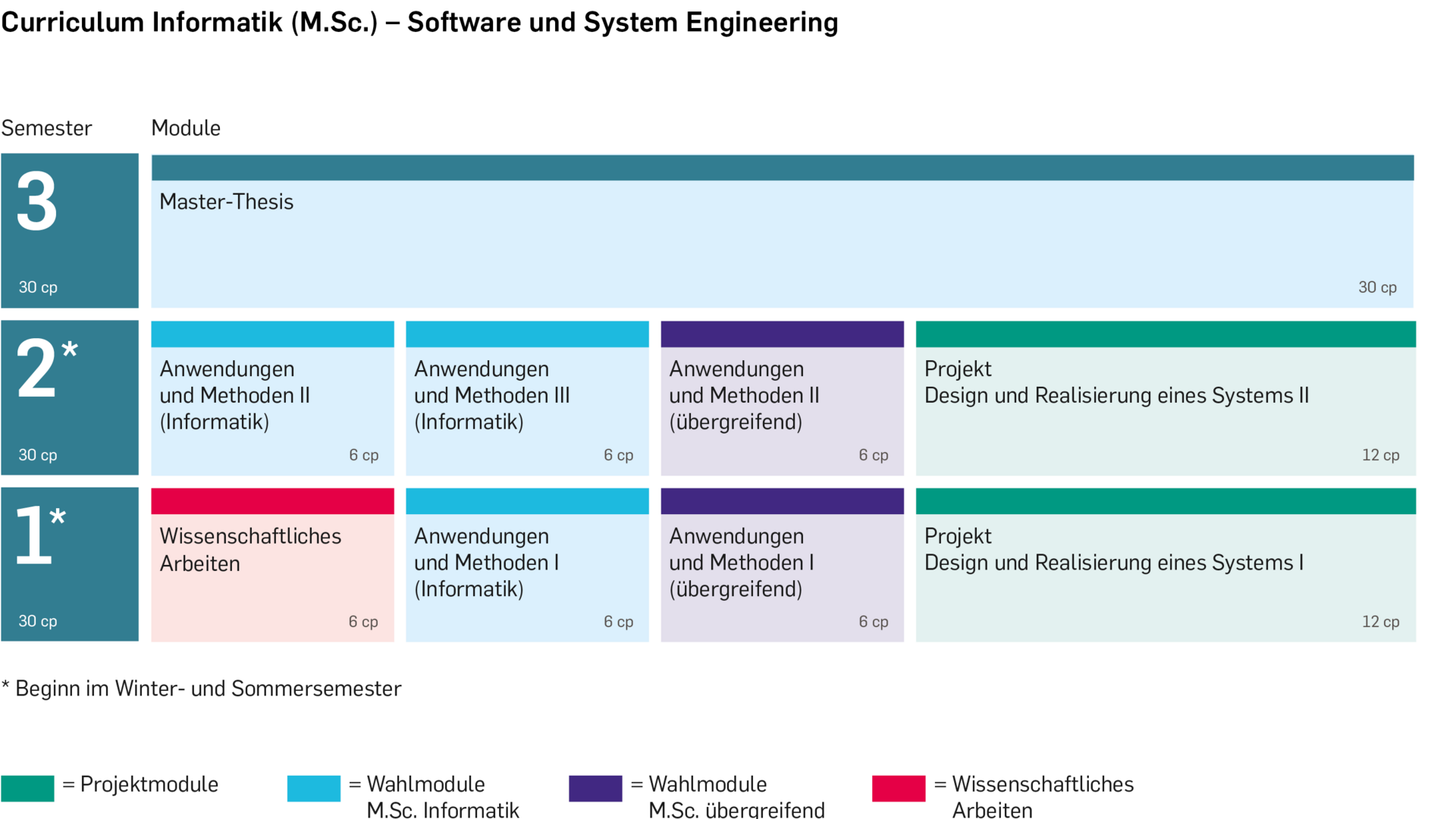
Studienverlauf
Das Studium umfasst ein Pflichtmodul, fünf Wahlpflicht-Module, zwei Projekt-Module und die Master-Thesis. Dabei können die Module der ersten beiden Semester in beliebiger Reihenfolge absolviert werden.
Modulhandbuch und Prüfungsordnung
Semestertermine
Die Semestertermine finden Sie auf der Seite des Studienbüros.
Informationen zum Studienstart und Semesterbeginn des Sommersemesters 2025
Liebe Erstsemester, liebe Studierenden,
unsere Einführungsveranstaltung findet am Dienstag, 15.04.2025 um 10:00 Uhr in Raum D 11, Gebäude D, Unter den Eichen sowie alternativ online über Zapp statt.
Zur digitalen Teilnahme benutzen Sie bitte den nachstehenden Link:
https://zapp.mi.hs-rm.de/meet/ulrich.schwanecke/Master-Info
Weitere Informationen zur Modulauswahl, Belegung und Beginn der Lehrveranstaltungen finden Sie im Begrüßungsschreiben für Erstsemester bzw. im Zeitplan für alle Master-Studiengänge oder am Aushang neben dem Sekretariat im 1.Stock des Gebäudes C-Nord.
Einen guten Semesterstart wünscht
Ulrich Schwanecke
Bitte beachten Sie, dass es zu kurzfristigen Änderungen kommen kann! Bitte überprüfen Sie regelmäßig unsere Website.

Hier geht es zum Informatikportal (Anmeldung mit HDS-Account notwendig)